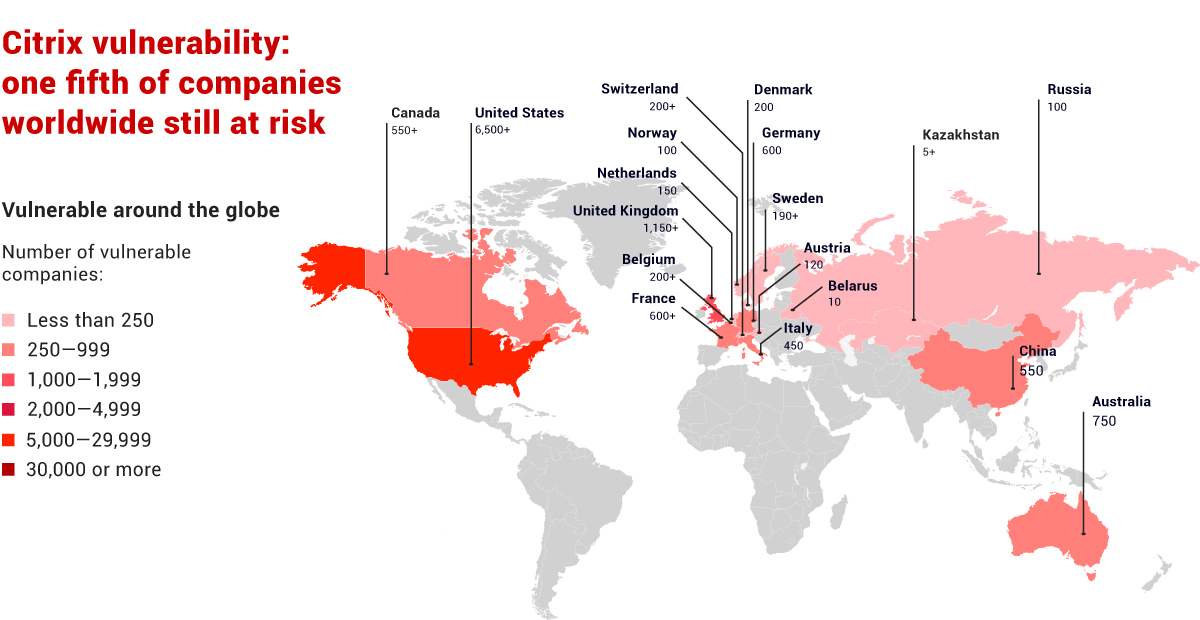
A month and a half after Positive Technologies released its overview of a critical vulnerability in Citrix software that was endangering 80,000 companies in 158 countries, one out of every five companies have still not taken any action to fix this vulnerability. This is evident from threat intelligence from Positive Technologies.
Critical vulnerability CVE-2019-19781 in Citrix Application Delivery Controller (NetScaler ADC)1 and Citrix Gateway (NetScaler Gateway) was discovered in December by Positive Technologies expert Mikhail Klyuchnikov. According to Positive Technologies data as of the end of 2019, the greatest number of potentially vulnerable organizations is located in the USA (over 38% of all vulnerable organizations), as well as in Germany, Great Britain, the Netherlands, and Australia. On January 8, 2020, an exploit was released. It allows the potential attacker to perform automatic attacks against companies that failed to fix the vulnerability.
"The Citrix developers planned to resolve the issue on January 27 through January 31, but released a series of patches for various product versions a week before that. The necessary update must be installed as soon as possible. Until then, follow the security recommendations by Citrix, available since the information about the vulnerability was released," says Alexei Novikov, Director of PT Expert Security Center.
Overall, the vulnerability is being fixed quickly, but 19 percent of companies are still at risk. The countries with the greatest numbers of vulnerable companies currently include Brazil (43% of all companies where the vulnerability was originally detected), China (39%), Russia (35%), France (34%), Italy (33%), and Spain (25%). The USA, Great Britain, and Australia are protecting themselves quicker, but they each have 21 percent of companies still using vulnerable devices without any protection measures.
Once again, if the vulnerability is exploited, attackers obtain direct access to the company's local network from the Internet. This attack does not require access to any accounts, and therefore can be performed by any external attacker.
To fend off potential attacks, companies can use web application firewalls. For example, PT Application Firewall can detect this attack out of the box. The system must be set to block all dangerous requests to ensure protection in real time. Considering how long this vulnerability has been around (since the first vulnerable version of the software was released in 2014), detecting potential exploitation of this vulnerability (and, therefore, infrastructure compromise) retrospectively becomes just as important. Starting December 18, 2019, PT Network Attack Discovery users can use special rules detecting attempts to exploit this vulnerability online.
- Citrix ADC is a software-oriented solution for delivering applications and balancing the load. It was specifically designed to increase the operation speed of traditional, cloud-based, and web-based applications, no matter where they are located. Stratistics MRC analysts expect the global market of this type of application delivery controllers to grow by 6.8 percent, reaching USD 4.98 billion by 2023. The analysts believe such controllers are already widespread, mostly in the IT and telecom industries. By 2023, the demand for ADCs for financial and insurance companies will increase. According to estimates by Citrix (Citrix Russia), by 2014 solutions of this type (NetScaler product line, back then) were used by about 75 percent of Internet users.
